What is traffic website ?
Just like traffic on a highway refers to the number of cars traveling down the road, web traffic is the number of web users who travel to any given website. Each person who logs on to a website is recorded as a visit or session, with a starting and ending point, thanks to behind-the-scenes communications between a user’s device and the website itself.
Web traffic is specific to each page of your website as well, so whether you have a one-page site or a 50-page site, each of those page’s traffic is configured independently of all other pages.
When you visit a Web site, the communications between your PC and the site’s server constitute Web traffic. The amount of traffic and the details of each visit are extremely valuable information to a Web-based business. The server computer records every request for a Web page, allowing its operators to determine which pages get the most attention. Web traffic analysis gives businesses concrete, reliable information on the interests of their customers.
How do you measure website traffic
There are numerous ways to measure website traffic, including:1 . Session numbers
This involves looking at the number of visits the website receives across a fixed period (one week, one month, etc.), to assess how effective traffic-building initiatives (SEO, PPC, etc.) have been since implementation.
2 . Purchase percentage
Online businesses selling products through their websites depend on purchases to succeed. Identifying the number of visitors making a purchase reveals how effective the site is in encouraging people to buy.
3 . Channels
Another way to measure website traffic is to find out which channels it comes through, such as email, organic search, email, etc.
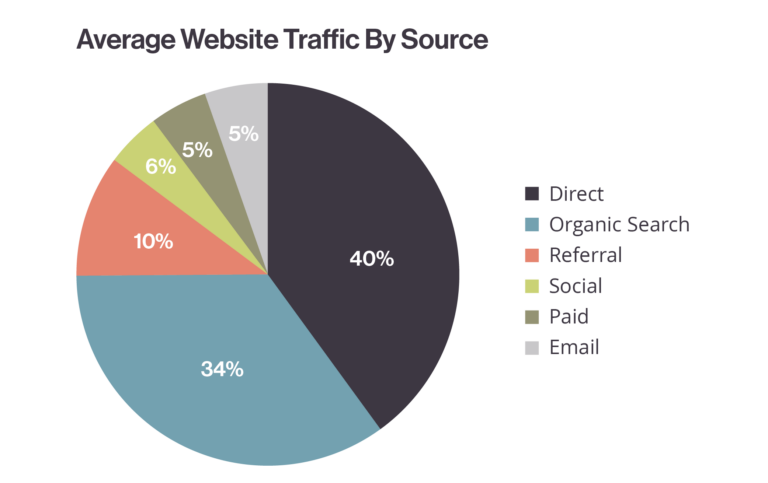
1.Organic Search Traffic
Organic traffic is the primary channel that inbound marketing strives to increase. This traffic is defined as visitors coming from a search engine, such as Google or Bing. This does not include paid search ads, but that doesn’t mean organic traffic isn’t impacted by paid search or display advertising, either positively or negatively. In general, people trust search engines, and sayings such as “just Google it” reinforce that humans are tied to the search engine. Thus, paid search, display, or even offline campaigns can drive searches, which may increase organic traffic while those campaigns are running.
That said, we also know that organic search traffic as a whole has been negatively impacted by the layout changes Google made to search results in recent years, which caused some websites such as Wayfair to see 25 percent of clicks on desktop and 55 percent on mobile be lost to paid search results.
To sum up all of this information, even organic traffic, like direct traffic, has some gray areas. For the most part, though, organic traffic is driven by SEO. The better you rank for competitive keywords, the more organic traffic will result. Websites that consistently create content optimized for search will see a steady increase in organic search traffic and improved positioning in search results. As a marketer, it is important to look at your keywords and high-ranking pages to identify new SEO opportunities each month.
Traffic data is a great way to take the temperature of your website and marketing initiatives. When you are writing and promoting blog content on a regular basis, you can use traffic data to track results and correlate these efforts to actual ROI. Be sure to look at website traffic numbers over long-term intervals to see trends and report on improvement over time.
2. Direct Traffic
Direct traffic is most often the result of a user entering a URL into their browser or using a bookmark to directly access the site. Essentially, Direct sessions occur any time Google Analytics cannot determine another referring source or channel. This differentiates Direct traffic from other default channel groupings like Organic, Referrals, Social, Email and Paid. However, Direct traffic may also consist of users who reached the site in other ways.
Other common instances of Direct traffic include:
- Clicking an untagged link from an email (depending on email provider/program)
- Clicking a link from a Microsoft Office or PDF document
- Accessing the site from a shortened URL (depending on the URL shortener)
- Clicking a link from a mobile social media apps like Facebook or Twitter. Mobile apps may not pass referrer information.
3.Referral Traffic
Referral traffic is traffic from other websites apart from Google’s own search engine. If you clicked on one of links here in this page and it led to another website, my website is counted as a referral traffic in their Google Analytic’s account. And it also works the other way around.
There are two distinctions that need to be clarified here.
First, if you search on Google and clicked on one of those results, you are technically coming from another website (Google’s). But, those searches are tracked under organic traffic. There will be instances when you’ll receive referral traffic from google.com such as those coming from forums or help center, regardless, if your traffic comes from search engines, that falls under organic traffic.
Next, traffic from social media also comes from another website, but because Google Analytics already has a special channel dedicated to it, it won’t be included in your referral traffic.
Traffic from other websites is a great source of quality leads. Unfortunately, most people in the marketing industry tend to neglect them because they are caught up in link building opportunities instead.
There are many ways that companies can increase their referral traffic using social media strategies. For instance:
Time your posts to ensure that you’re sharing your posts when your followers are most active.
Use a scheduling calendar like Sprout Social’s to maintain consistency in your sharing.
Use social media plugins on your website to enable easy social sharing.
Make your content as visual as possible. Social posts with images lead to up to 650% more engagement than posts with text alone.
4. Social Traffic
Traffic refers to all visits a user makes to a website or a mobile application. Social traffic is all traffic directed to a website or mobile site from social networks and social media platforms.
Social traffic may be either paid traffic or organic traffic, depending on the marketing campaigns, paid advertising and social media platforms available to users.
Benefits of social traffic include:
- Better conversion rate
- More inbound traffic
- Brand awareness
Increasing your social media traffic happens when you engage and build relationships on each network. Being readily available for customers, brand loyalists and potential buyers it helps you nurture these people through the purchasing process.
5. Paid Traffic
Paid traffic from search engines arrives to websites when a user clicks on an advertisement placed on a SERP for a given search term. This ad is created and paid for by a company – with the aid of an ad platform – seeking to appear first in search engines.
As you can see, the goal of both organic and paid traffic campaigns is the same: to be clicked on more often than anyone else competing for the same search term.
Paid search advertising exists inside an automated open-auction bidding platform such as Google Ads. Google sets a price for a keyword and companies bid on that keyword. Google then:
Evaluates your maximum bid (often measured as pay-per-click, or PPC).
Assesses the relevance of your proposed ad as it relates to the term being bidded on.
Assigns a Quality Score, a measurement of click-through rate, landing page quality and ad relevance.
Type of paid traffic :
- Pay per click or per impression
- Paid or sponsored posts
- Influencer marketing
- Buying targeted traffic
- Paid directory listings
6. Email Marketing Traffic
In digital marketing, email traffic refers to the visitors driven to a website via email marketing campaigns. It is one of the most valuable traffic as it comes from your existing as well as new leads and customers, thus strengthening the bond between you and the clients. It not only brings the highest ROI (Return of Investment) across different channels but also continuously keeps your current leads and clienteles engaged.
Uses of Email Traffic
Email traffic tells you how engaged your current leads and customers are.
It’s a great indication of which messaging is working in your email marketing.
If you are using different marketing emails and tracking them properly, you can see the performance of them in your Google Analytics account.
5 Tips for Increase Email Traffic
- Continuously build your email list
- Don’t rely on newsletter signups as your lead generation
- Send relevant email
- Don’t forget to add UTM tags
conclusion
There are 4 Billion Internet users. Imagine that! The larger the number of visitors to your website the better! When you can increase your traffic along with the quality of the visitors, the better you will be able to increase your website conversion and get that traffic to become paying customers.
Other than making money, more website traffic, in the long run, can allow you to expand your business and your business profits, hire more employees, increase your offerings, etc.